EicOsis is Developing a New Way to Effectively Treat Pain and Inflammation
We are developing a completely new class of non-opioid, oral treatment for inflammatory and neuropathic pain. Our drugs treat pain by stabilizing natural pain-relieving and anti-inflammatory molecules.
EicOsis Human Health
EicOsis is developing a new class of oral drugs for human pain and inflammatory conditions. EC5026, our first candidate drug, is currently undergoing Phase 1 human clinical trials. Learn more about EC5026 and our pipeline.
Evidence for Efficacy in Pain and Inflammation
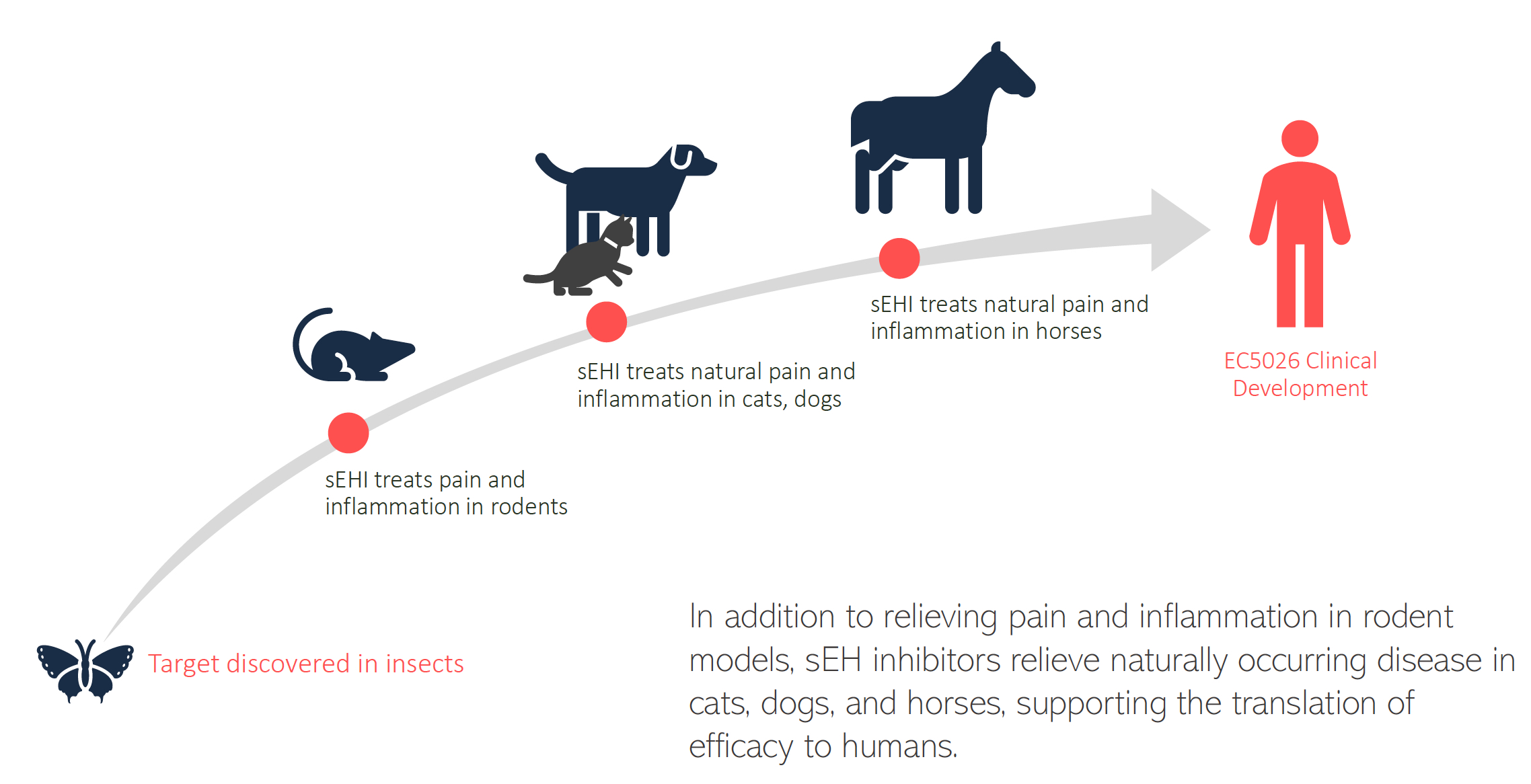
In addition to showing efficacy in rodent models, sEH inhibitors relieve naturally occurring pain and inflammation in cats, dogs, and horses, supporting the translation of efficacy to humans.
Research & Publications
The scientific developments behind sEH inhibitors are the result of more than 30 years of research. Access our scientific publications and learn more about the effects of sEH inhibition for the treatment of pain.
A New Target for Pain Relief and Inflammation: the soluble Epoxide Hydrolase Enzyme (sEH)
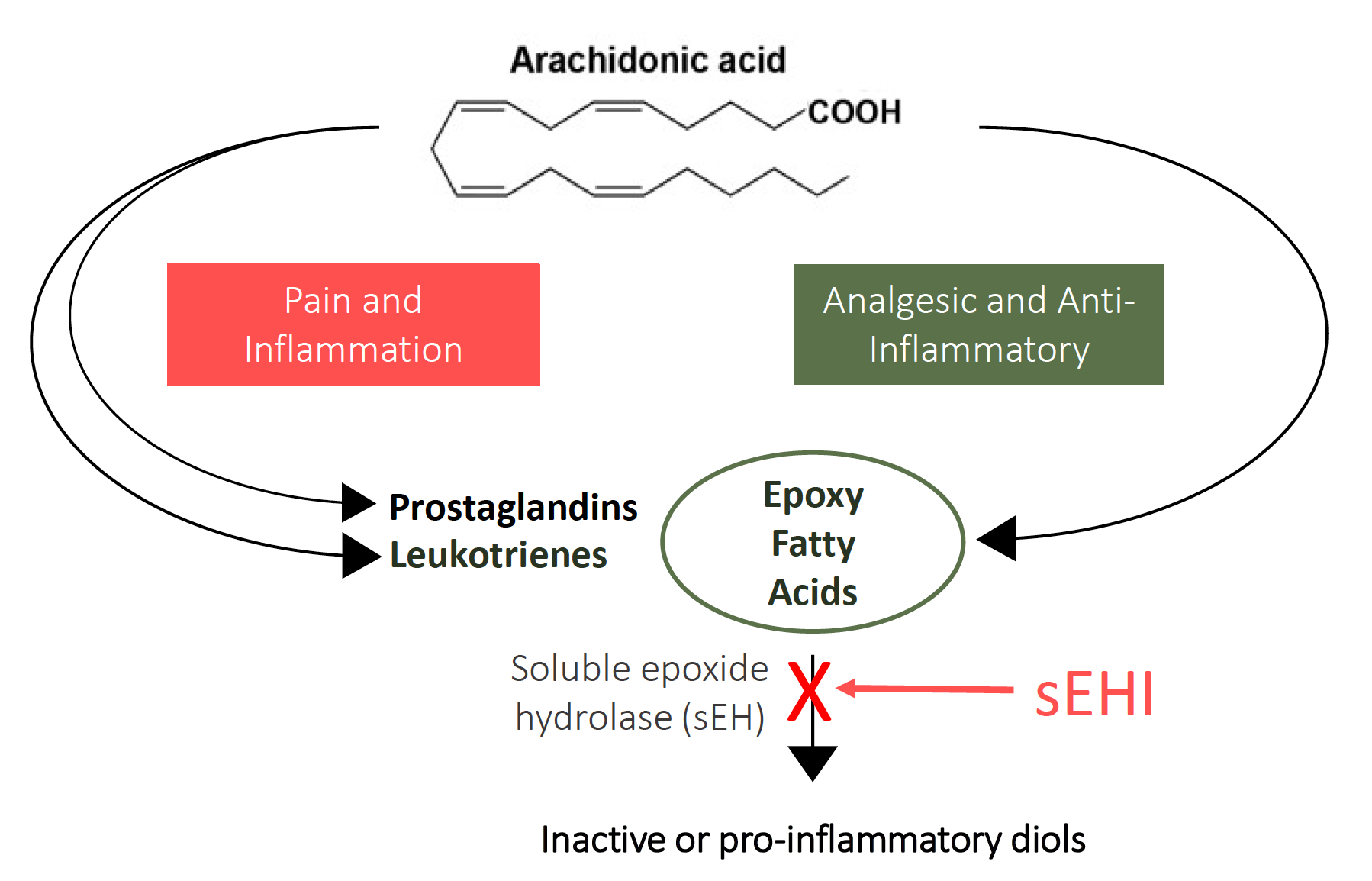
The soluble Epoxide Hydrolase (sEH) enzyme regulates the activity of powerful anti-inflammatory fatty acids called Epoxy-fatty acids (EpFA) that are present in all cells in humans and animals. EpFAs have analgesic and anti-inflammatory properties, but are short-lived molecules that are normally eliminated within seconds. By inhibiting sEH, EpFA levels can be increased and maintained at high anti-inflammatory and analgesic levels for 24 hours or longer. Learn more about the science behind sEH inhibition.
Inhibiting sEH Relieves Pain and Inflammation Effectively
sEH inhibitors treat pain and inflammation by increasing the body’s natural anti-inflammatory mediators without severe adverse side-effects common to currently available analgesics and anti-inflammatories. sEH inhibitors are designed for once daily oral dosing.